Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) in Ladakh
Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) in Ladakh

Sangay Lamo
Research Intern, IISD
IISD Research and Knowledge Support Center
for Sustainable Development in Ladakh
The sustainable development goals by 2030 agenda undertaken in September 2015 at a
historic UN submit calls for urgent action to be taken by all countries both developed and
developing countries for sustainable development. In the sustainable development goals,
SDG 13 talks about disaster risk reduction where it provides an opportunity to all the
countries to align its developmental goals with disaster risk reduction related objectives and
giving priority to risk reduction with a global target. As a signatory to SDGs, it is the primary
responsibility of India to fulfil its commitments by 2030 to strengthen its resilience to combat
natural disasters and in building back better.
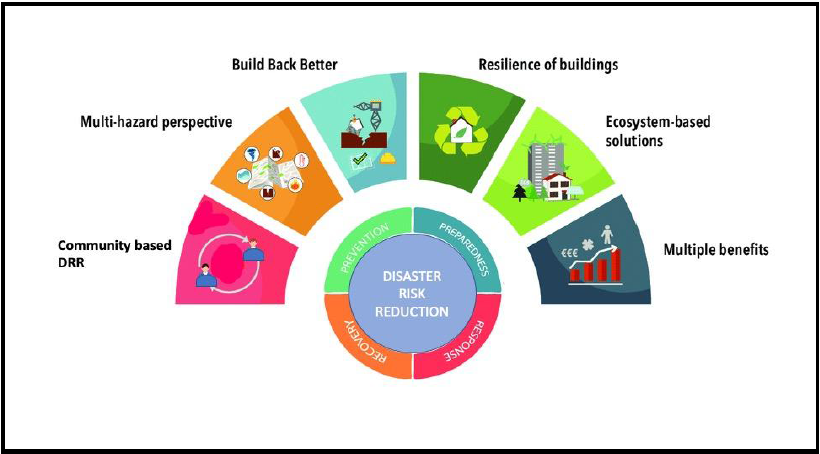
Disaster risk reduction is a systematic approach that identifies multiple-hazard perspectives
and assesses in reducing the risk of a disaster. Its primary aim is to reduce the
socio-economic vulnerabilities to disaster as well as dealing with the environmental and
other hazards and exposure to the hazard. The activities and measures in disaster risk
reduction includes, identification of disaster and measuring its risk, education and knowledge
development, providing information to people about their risk and creating risk awareness,
incorporating disaster risk management into national planning and investments,
strengthening the institutional arrangements and legislative frameworks for disaster risk
reduction, providing financial protection to the vulnerable people who are at risk and
integrating disaster risk reduction across multiple sectors which includes health, transport,
environment etc.
Since the severity of natural hazards cannot be reduced, the main objective of disaster risk
reduction lies in reducing vulnerabilities and exposure, thus reducing these two components
of risk requires identifying and reducing the underlying drivers of risk, which are particularly
related to poor economic development and practises, rapid degradation of the environment,
poverty, rising climate change, inequality which exacerbate conditions of hazard, exposure,
risk and vulnerability.
Thus, the focus should be given on risk management rather than just disasters. As disaster
risk reduction talks about sustainable development which avoids the construction of new
risks, address the pre-existing risks and share risk prevention strategies to minimise loss
and injuries by creating awareness and by adopting a people-centred approach and
community based approach for building resilience which helps in disaster prevention. The
rising attention to the role of community in the risk management cycle and people centred
approach in disaster risk management has emerged in recent years creates a bridge
between the institutional policies and plans with the role of the communities in shaping their
own surroundings. Community-based disaster risk management focuses on the risk
management of the communities by engaging the vulnerable communities actively in the
identification, analysis, treatment, monitoring and evaluation of disaster risks in order to
reduce their vulnerabilities and enhance their capacities. This means that people or the
community who are at risk can take part in decision making and implementation of disaster
risk management activities.
A community based disaster risk management thus helps in response to local problems and
needs as it integrates the local knowledge and practises with adoption of their knowledge
(which are sustainable in nature) helps in strengthening the community’s capacity to tackle
future disasters
Engagement of local communities of Ladakh in disaster risk reduction will help in better
preparedness and emergency response action, as local communities are the first responder
in a disaster situation. They respond before the arrival of the response team in search and
rescue and also provide immediate assistance to the injured and homeless. A process of
building capacity and generation of public awareness exercises must be taken among the
local communities before the occurrence of a disaster to make disaster risk management
inclusive and effective. Communities should be provided with skills, training, knowledge,
resources and capacities to engage in disaster risk management especially the small-scale
localised sector and the community which are at high risk to disasters. Community-based
disaster risk management thus helps in minimising the use of resources by providing better
opportunities and skills to the local community with the use of local techniques and materials
in managing a disaster situation and making them more resilient to future disasters.
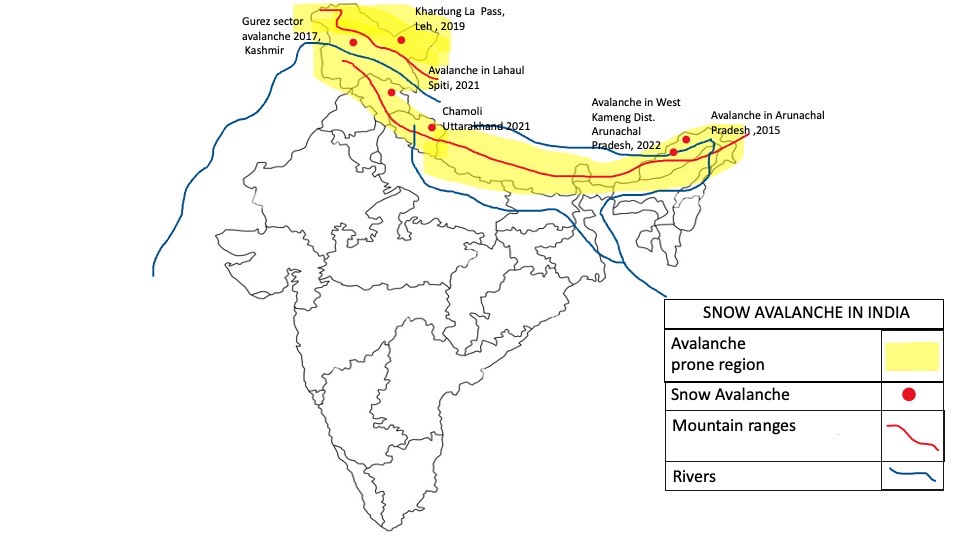
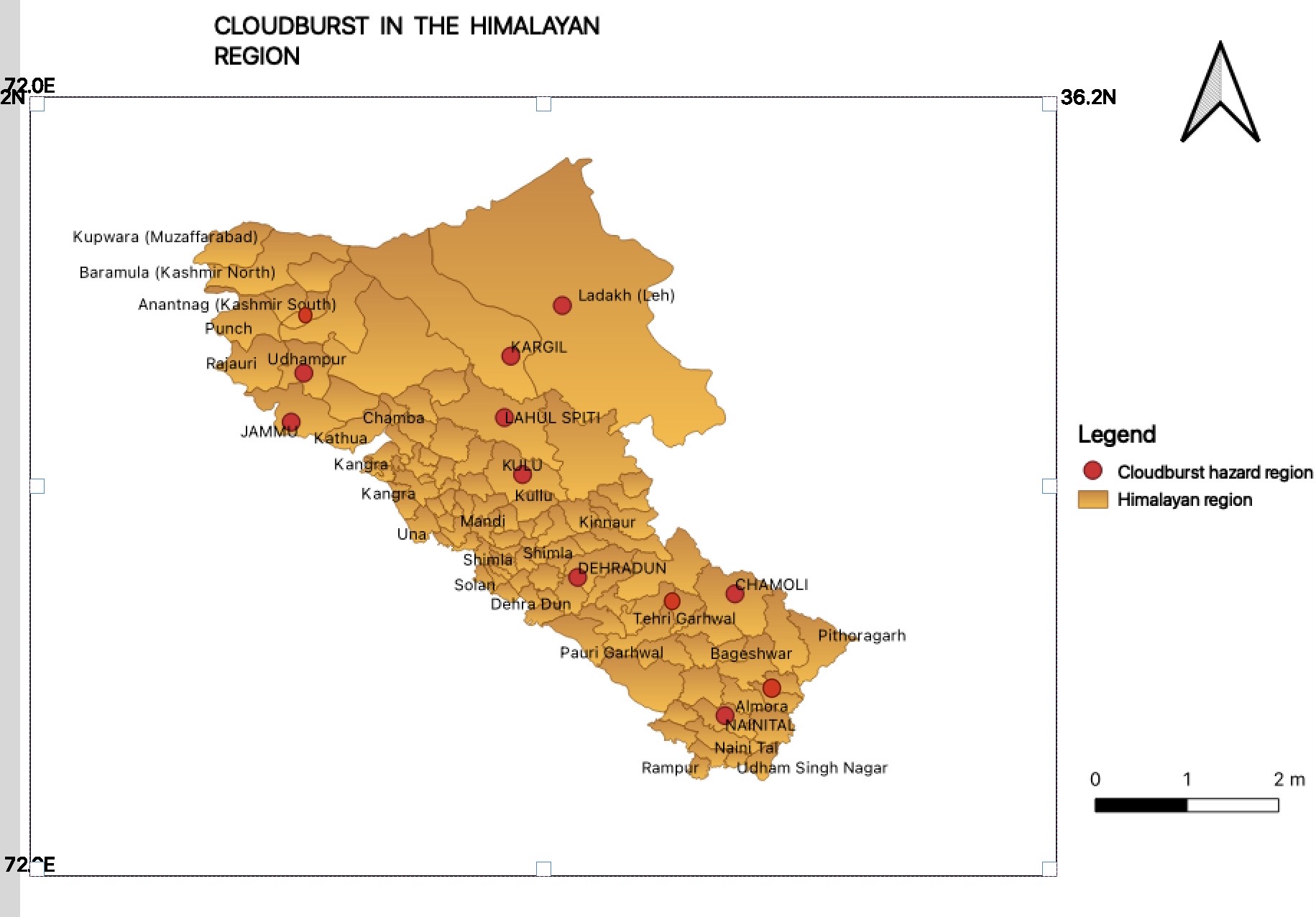
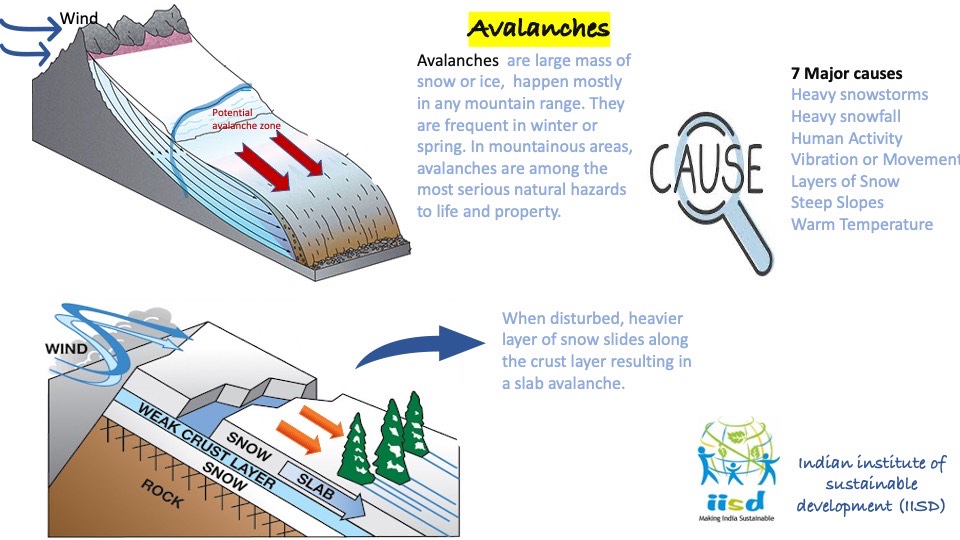
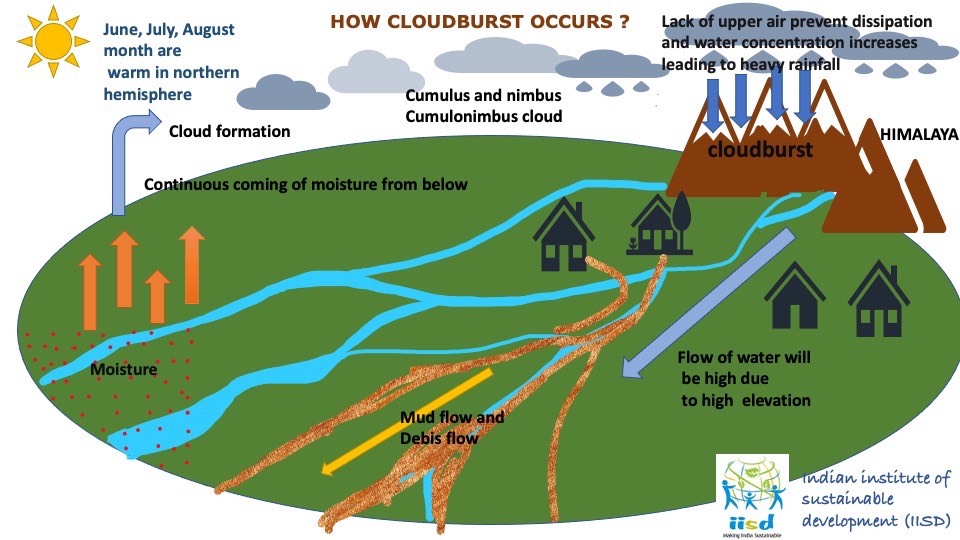
When a disaster strikes, we are immediately drawn to the human suffering cost. During the
2010 cloudburst, the scale of suffering was breathtaking; more than 250 people died in
hazard. The Leh cloudburst of 2010, the cloud burst of 2020 in Kargil, the constant incidence
of avalanches in the glacial region, and the recent outbreak of foot and mouth disease in
Duchik village are some of the powerful examples of how emergencies not only impact
people's health but also the society and livelihood at large scale. But much of this immediate
and post-disaster pain, as well as the terrible structural damage inflicted on hospitals,
infrastructures, BSNL office, and other vital services are avoidable through intensified
government actions on disaster risk management. While running a healthcare system is
expensive, rebuilding those destroyed healthcare systems by a disaster is even many times
more costly.
Disaster impacts are more devastating when they occur in low income countries. The risk of
dying and damages multiplies many times greater in low income countries than in a
developed nation. There are many factors which make the community in low income
countries more vulnerable to disasters because of poor health care systems, weak
infrastructure and lack of disaster risk management capacities. Thus, focus should be given
to the advancement of early warning systems that can protect an alert population in
advance which are rare in places that are poorly developed. There should also be a given
focus to community engagement with disaster management to facilitate various stakeholders
which are working together in disaster management to build resilience through collaborative
actions, capacity building measures and development of strong relationships built on mutual
trust and respect.
An ecosystem approach for disaster risk reduction
Ladakh being an eco-fragile region, the consequences of climate change doubles due to its
fragile ecosystem. As in the past few years with the rise in climate change there has been a
rapid melting of glacial snow, rise in temperature, increase in carbon emission and
intensified greenhouse gases which not only impacted the society but also the delicate
environment.
Thus an ecosystem approach is needed to be adopted in disaster risk reduction for
integration in management of fragile land, water and living resources to promote
conservation and sustainable use of resources in an equitable way. Ecosystem acts as a
buffer against natural disasters and helps in preventing, reducing the impact of disaster on
people, critical infrastructure and basic services. Conservation of the fragile ecosystem,
restoration and sustainable use of the available resources, such measures are needed to be
adopted to strengthen disaster risk management. Ecosystem approach helps in disaster risk
reduction as it includes proper plans and policies by giving priority to the ecosystem like
supporting, provisioning, regulating and cultural services. Adoption of ecosystem approach
will help in implementation of proper strategy for disaster risk reduction with integration of
management of land, water and resources. Ecosystem approach will help in reducing
disaster risk as it is a conceptual framework for resolving issues related to the ecosystem
and with the rising problems in Ladakh, an ecosystem approach is a must for preservation of
the fragile ecosystem as well as for proper implementation of management of resources.
The application of the approach will help in reaching a balance between conservation,
sustainability, fair and equitable share of resources and benefit of the society by sustainable
utilisation of genetic resources.
The benefits that people of Ladakh will get by adoption of ecosystem approach are
-
It will provide supporting services as ecosystem services are an overarching service
which is necessary for the production of other ecosystem services such as
production of biomass, water cycle and carbon sequestration.
- It will also provide provisioning services or the ecosystem goods which supports
livelihoods like providing proper food, fresh water, food and fiber.
- It will help in regulating services for protection of the environment in which people
reside. It will also give cultural services as these are the services which provide
support and services like spiritual values, aesthetic needs, educational needs and
recreational needs.
The Ecosystem approach is cost-effective and helps in building natural infrastructure with
larger capacity to withhold extreme climatic conditions, it will help in preserving biodiversity
with proper adoption of sustainable plans and policies. The approach will be people centric
which will help the people of Ladakh in dealing with extreme climatic conditions by providing
proper livelihood and by providing cultural services like spiritual values, educational needs
and providing moral support. Thus ecosystem-based disaster risk reduction will help in
regulating services at a larger portion with less utilisation of economy as it is cost effective
and will give priority to control services. It will help in providing values to the damage to the
environment as well as to the people affected by extreme climatic conditions.
___________________________
Ms. Sangay Lamo is a Research Intern, at IISD
Knowledge Support Center for Sustainable Development in Ladakh.

Community-based disaster risk management